Introduction¶
Automation Overview¶
This training workshop provides hands-on exposure to the three primary categories of infrastructure automation activities: Build, Run, and Respond.
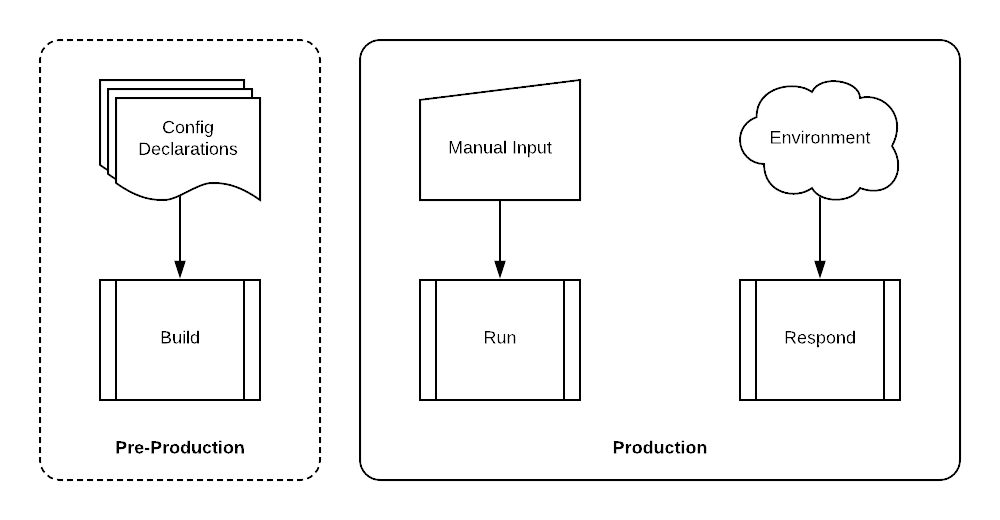
- Build
- Build automation is the means by which a set of infrastructure elements are declared, instantiated, and orchestrated using automation tools and infrastructure APIs. The result is a set of deployed infrastructure elements that are in production (or production-ready) with a “day one” configuration.
- Run
- Run automation encompasses any API-based configuration management actions that occur once the infrastructure element is in production. These are primarily scheduled changes that are made to support new requirements. The input to these changes is manually defined in a variety of formats such as YAML, JSON, XML, etc.
- Respond
- Response automation includes any automated actions that are triggered by an event. These may be operational events such as changes to the infrastructure or security events such as of a new threat. Response actions are defined in advance but only initiated when a event matching its trigger criteria occurs.
Lab Topology¶
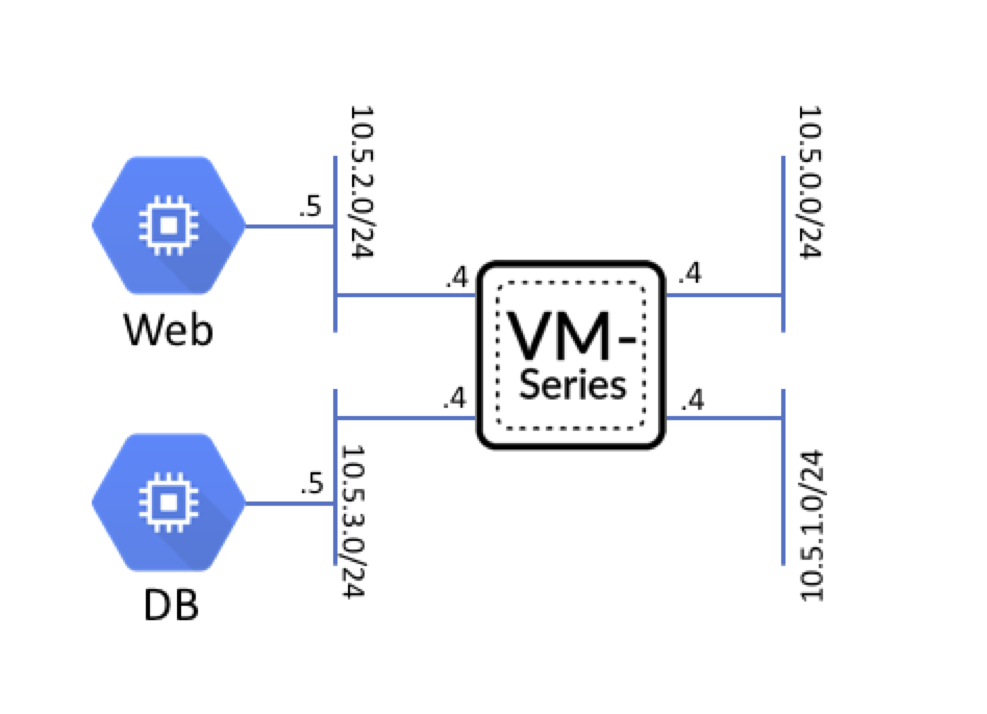
| Subnet | Address | Interface |
|---|---|---|
| Management | 10.5.0.0/24 | Management |
| Untrust | 10.5.1.0/24 | ethernet1/1 |
| Web | 10.5.2.0/24 | ethernet1/2 |
| Database | 10.5.3.0/24 | ethernet1/3 |
Lab Components¶
- Qwiklabs
- This lab is launched using Qwiklabs, which is an online learning platform that deploys and provides access to cloud-based lab environments. Qwiklabs will establish a set of temporary set of credentials in the cloud provider in order to deploy and access the cloud infrastructure and services.
- Launchpad VM
- A Debian 9 Linux virtual machine will be deployed in each cloud environment for you to use as your primary workspace for the lab activities, This VM will be provisioned with all the tools and libraries necessary for deploying and managing infrastructure in the cloud provider.
- Hashicorp Terraform
- Each cloud provider offers a mechanism that allow you to define a set of infrastructure element or services and orchestrate their instantiation. However, these tools and templates are specific to each cloud provider. We will be using Terraform to perform this function as it provides a common set of capabilities and a template formats acroos all cloud providers.
- Red Hat Ansible
- Whereas Terraform excels at orchestrating deployment activities, Ansible is more effective at automating configuration management tasks. We will be using both Terraform and Ansible to make configuration changes to the VM-Series firewall in order to illustrate their different capabilities.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Google Cloud Platform, offered by Google, is a suite of cloud computing services that runs on the same infrastructure that Google uses internally for its end-user products, such as Google Search and YouTube.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Amazon Web Services is a subsidiary of Amazon that provides on-demand cloud computing platforms to individuals, companies and governments, on a metered pay-as-you-go basis.